Leptin Ghrelin Insulin Explained: The Trio Behind Your Eating Habits
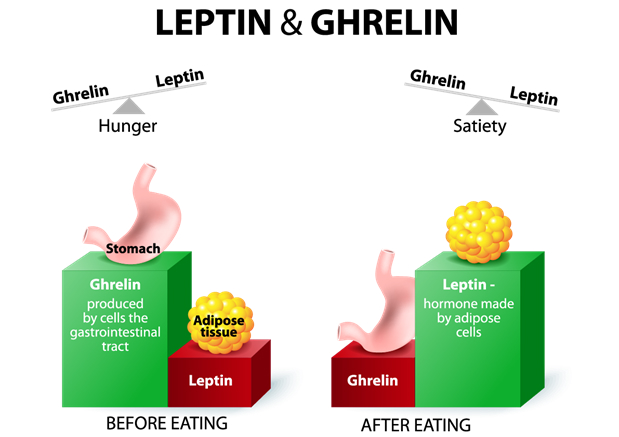
Table of Contents

Jumpstart Your Weight Loss in Just 7 Days!
Download our Free 7-Day Weight Loss Kickstart PDF to plan your meals, hydration, movement, and mindset for rapid, sustainable results.
Download Free PDF NowAppetite Hormones: The Hidden Regulators of Your Hunger
Ever wonder why you feel hungry even after eating, or why cravings hit hard late at night? The answer often lies in your appetite hormones. These chemical messengers silently control when you feel hungry, full, or completely out of control around food.
In this guide, we’ll break down leptin, ghrelin, and insulin in a simple, beginner-friendly way. You’ll learn how these hormones interact, why they sometimes stop working properly, and how they directly impact weight gain and weight loss.
No medical jargon. No confusing science. Just a clear explanation of how appetite hormones really work — and how to use that knowledge to eat smarter.
Leptin Hormone: The Satiety Signal That Tells Your Brain You're Full
The leptin hormone is one of the most important appetite hormones in the human body. It acts as a long-term regulator of energy balance by telling your brain when you’ve eaten enough and when your fat stores are sufficient.
Leptin is produced mainly by fat cells and released into the bloodstream. Once it reaches the brain, it sends a powerful signal to reduce hunger and increase energy expenditure.
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), leptin plays a central role in appetite regulation, metabolism, and body weight control.
When leptin signaling works properly, your body naturally balances food intake with energy needs. But when this signaling system breaks down, hunger and cravings can persist even when your body has enough stored energy.
How Leptin Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown for Beginners
To clearly understand appetite hormones, it’s essential to know exactly how leptin works. Below is a simple, beginner-friendly breakdown of the leptin signaling process.
- Fat cells release leptin: As fat stores increase, fat cells produce more leptin and release it into the bloodstream.
- Leptin travels to the brain: Leptin crosses the blood-brain barrier and reaches the hypothalamus, the brain’s appetite control center.
- The brain receives the fullness signal: When leptin receptors function correctly, the brain reduces hunger signals and increases satiety.
- Food intake naturally decreases: Appetite drops, cravings fade, and energy balance stabilizes.
Research from Healthline confirms that leptin is essential for long-term appetite regulation, not short-term hunger control.
Unfortunately, many people develop a condition known as leptin resistance, where the brain no longer responds properly to leptin signals. This leads to constant hunger despite high leptin levels.
Studies published in Endocrine Reviews show that leptin resistance is strongly associated with obesity, chronic dieting, inflammation, and poor sleep.
This explains why simply “eating less” often fails — the issue isn’t willpower, but broken hormonal signaling.

Discover the Best Natural Belly Fat Burner!
Check out our detailed review of the top belly fat supplement for 2026. Learn what works, what doesn’t, and how to maximize results safely.
Read Full ReviewGhrelin Hormone: The "Hunger Switch" That Kicks In When You're Starving
The ghrelin hormone is commonly known as the hunger hormone. It plays a crucial role in short-term appetite regulation by signaling your brain when it’s time to eat.
Unlike leptin, which signals fullness, ghrelin works in the opposite direction. When ghrelin levels rise, hunger increases — and when levels fall, appetite decreases.
According to research published by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), ghrelin is produced mainly in the stomach and directly stimulates appetite by acting on the hypothalamus.
Ghrelin Hunger Hormone: Why It Peaks Before Meals
One unique feature of the ghrelin hunger hormone is its predictable daily rhythm. Ghrelin levels naturally rise before meals and fall shortly after eating.
This is why hunger often feels intense at specific times of the day — even if you’ve eaten enough calories overall. Your body is responding to hormonal signals, not a lack of willpower.
A study from The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that ghrelin levels increase significantly before meals and drop rapidly after food intake.
This mechanism explains why structured meal timing can help regulate appetite and reduce impulsive eating.
What Triggers High Ghrelin Levels?
Several lifestyle and dietary factors can cause ghrelin levels to rise excessively, making hunger harder to control.
- Calorie restriction: Very low-calorie diets dramatically increase ghrelin.
- Skipping meals: Irregular eating patterns confuse hunger signals.
- Lack of sleep: Poor sleep increases ghrelin and reduces leptin.
- Chronic stress: Stress hormones amplify hunger signals.
Research from Sleep Foundation confirms that sleep deprivation significantly increases ghrelin levels and appetite the next day.
Why Extreme Dieting Backfires: Ghrelin’s Survival Response
One of the biggest mistakes beginners make is assuming hunger is a weakness. In reality, high ghrelin levels are a biological survival response.
When you drastically reduce calories, your body interprets it as starvation. Ghrelin spikes, metabolism slows, and cravings intensify — making long-term dieting unsustainable.
According to a long-term study published in Obesity Reviews, ghrelin levels can remain elevated for months after weight loss, explaining why rebound weight gain is common.
This is why sustainable eating strategies outperform aggressive diets when it comes to appetite control.
Insulin Appetite: How Blood Sugar Swings Trigger Cravings
The connection between insulin appetite and hunger is often misunderstood. Insulin is not just a blood sugar hormone — it plays a direct role in how hungry you feel, how often cravings appear, and how your body stores fat.
Every time you eat carbohydrates, your blood sugar rises. In response, your pancreas releases insulin to move glucose into your cells for energy. When this process is balanced, appetite stays stable. When it isn’t, hunger and cravings spike.
According to the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), rapid blood sugar fluctuations increase appetite and promote overeating.

Want a Natural Way to Support Your Wellness?
Explore our comprehensive review of All-Day Slimming Tea to see how it can fit into your healthy routine — benefits, ingredients, and tips you should know.
Read Full Tea ReviewRole of Insulin in Hunger Control: Balancing Carbs for Steady Energy
The role of insulin in hunger control depends heavily on the type and timing of carbohydrates you consume.
Highly refined carbs and sugary foods cause a rapid spike in blood glucose, followed by a sharp insulin release. This often leads to a blood sugar crash — triggering intense hunger shortly after eating.
Research published in Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health shows that low–glycemic foods promote better appetite regulation and longer-lasting satiety.
Stable insulin levels help prevent emotional eating and reduce constant snacking.
Insulin Resistance and Appetite: Why You Feel Hungry Even After Eating
When cells become less responsive to insulin — a condition known as insulin resistance — glucose remains in the bloodstream instead of entering cells efficiently.
As a result, the brain interprets this as a lack of energy and signals hunger, even though calories are available. This creates a cycle of overeating, fatigue, and fat storage.
According to the American Diabetes Association, insulin resistance is a key factor in increased appetite and weight gain.
How to Stabilize Insulin Naturally for Better Appetite Control
Improving insulin sensitivity doesn’t require extreme dieting. Small, consistent habits can dramatically improve appetite regulation.
- Pair carbs with protein and fiber: slows glucose absorption.
- Avoid liquid sugars: they spike insulin rapidly without satiety.
- Move after meals: light walking improves insulin response.
- Prioritize sleep: poor sleep worsens insulin sensitivity.
A review in Nutrients Journal confirms that lifestyle interventions significantly improve insulin sensitivity and appetite control.
Leptin Ghrelin Insulin Explained: How These Hormones Work Together
Appetite is never controlled by a single hormone. Leptin, ghrelin, and insulin constantly communicate to regulate hunger, fullness, and energy balance.
When insulin is stable, leptin signals are clearer, and ghrelin spikes become less intense. But when insulin resistance develops, leptin signaling weakens, and ghrelin-driven hunger increases.
This hormonal imbalance explains why many people struggle with weight loss despite eating fewer calories.
How Leptin Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown for Beginners
Understanding how leptin works helps explain why some people feel full easily while others struggle with constant hunger, even after large meals.
Leptin is often called the “satiety hormone” because it tells your brain when you’ve had enough to eat. It is produced mainly by fat cells and acts as a long-term regulator of appetite and body weight.
Step 1: Fat Cells Release the Leptin Hormone
The leptin hormone is secreted by fat cells based on how much energy your body has stored. Higher fat stores usually mean higher leptin levels.
This signal is sent through the bloodstream to the brain, particularly to the hypothalamus — the control center for hunger and metabolism.
Source: NCBI – Leptin Overview
Step 2: The Brain Receives the “I’m Full” Signal
Once leptin reaches the hypothalamus, it binds to leptin receptors and signals that the body has sufficient energy.
This leads to:
- Reduced hunger signals
- Increased calorie burning
- Lower motivation to eat
In healthy individuals, this system works automatically without conscious effort.
Step 3: Leptin Suppresses Ghrelin (The Hunger Hormone)
One of leptin’s most important roles is suppressing the ghrelin hunger hormone.
When leptin levels are adequate, ghrelin secretion drops, meaning you feel satisfied and less food-focused.
Research published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism confirms this inverse relationship between leptin and ghrelin.
Step 4: Energy Balance Is Maintained Over Time
Unlike ghrelin, which fluctuates throughout the day, leptin works as a long-term energy regulator.
It helps maintain body weight by adjusting appetite and metabolism based on fat storage trends over weeks and months.
This explains why extreme calorie restriction often backfires — leptin levels fall, increasing hunger and slowing metabolism.
Leptin Resistance: When the Satiety Signal Stops Working
Many people struggling with weight gain don’t lack leptin — they suffer from leptin resistance.
In this state, leptin levels are high, but the brain no longer responds properly. The result is constant hunger, reduced energy expenditure, and stubborn fat storage.
According to NIH research, inflammation, poor sleep, and insulin resistance are key contributors to leptin resistance.
Common Signs of Leptin Resistance
- You feel hungry shortly after eating
- Cravings are frequent and intense
- Weight loss becomes increasingly difficult
- Energy levels remain low despite adequate calories
Frequently Asked Questions About Appetite Hormones
1. What are appetite hormones?
Appetite hormones are chemical messengers that regulate hunger, fullness, and energy balance. The most important ones are leptin, ghrelin, and insulin.
2. What is leptin hormone?
Leptin hormone is produced by fat cells and signals the brain that you have enough stored energy, helping reduce appetite.
3. What is ghrelin hunger hormone?
Ghrelin is known as the hunger hormone. It increases appetite and peaks before meals, signaling your body that it’s time to eat.
4. How do appetite hormones affect weight loss?
When appetite hormones are balanced, hunger is controlled and fat loss becomes easier. Hormonal imbalance can lead to overeating and stalled weight loss.
5. How leptin works in simple terms?
Leptin works by telling your brain that you’re full and don’t need more food, helping regulate long-term energy balance.
6. What causes leptin resistance?
Leptin resistance is caused by chronic inflammation, lack of sleep, insulin resistance, and long-term overeating.
7. Can high leptin levels still cause hunger?
Yes. In leptin resistance, leptin levels are high but the brain doesn’t respond properly, leading to continued hunger.
8. What foods support healthy leptin levels?
Protein-rich foods, whole vegetables, healthy fats, and fiber help improve leptin sensitivity.
9. How does sleep affect appetite hormones?
Poor sleep lowers leptin and increases ghrelin, making you feel hungrier and crave high-calorie foods.
10. What is insulin appetite connection?
Insulin regulates blood sugar. Frequent spikes can trigger hunger and cravings even when energy needs are met.
11. Role of insulin in hunger control?
Insulin helps move glucose into cells. Stable insulin levels help prevent sudden hunger and energy crashes.
12. Does sugar affect appetite hormones?
Yes. Excess sugar causes insulin spikes, increases ghrelin, and worsens leptin resistance over time.
13. Can stress increase hunger hormones?
Chronic stress raises cortisol, which disrupts leptin signaling and increases appetite.
14. Why do cravings happen at night?
Late-night cravings are often linked to disrupted ghrelin rhythms, poor sleep, and unstable blood sugar.
15. Are appetite hormones different for men and women?
Yes. Hormonal cycles, estrogen levels, and body fat distribution can affect appetite hormone responses.
16. Can exercise improve appetite hormone balance?
Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps normalize leptin and ghrelin levels.
17. Does fasting affect ghrelin hormone?
Short-term fasting may increase ghrelin initially, but levels often adapt over time with consistency.
18. Can supplements regulate appetite hormones?
Some supplements may support hormonal balance, but lifestyle changes remain the most effective approach.
19. Simple explanation of leptin and ghrelin?
Leptin tells you to stop eating, while ghrelin tells you to start. Together, they regulate hunger and fullness.
20. How long does it take to fix appetite hormone imbalance?
With proper sleep, diet, and stress control, improvements can be noticed within a few weeks.

Ready to Transform Your Health?
Take the first step now! Grab our Free 7-Day Weight Loss Kickstart PDF and start building a routine that actually works.
Get Your Free PDF